Diabetes and Insulin
-
The Share of Ozempic Users with Diabetes has Decreased Over Time, Indicating Increased Off-label Use
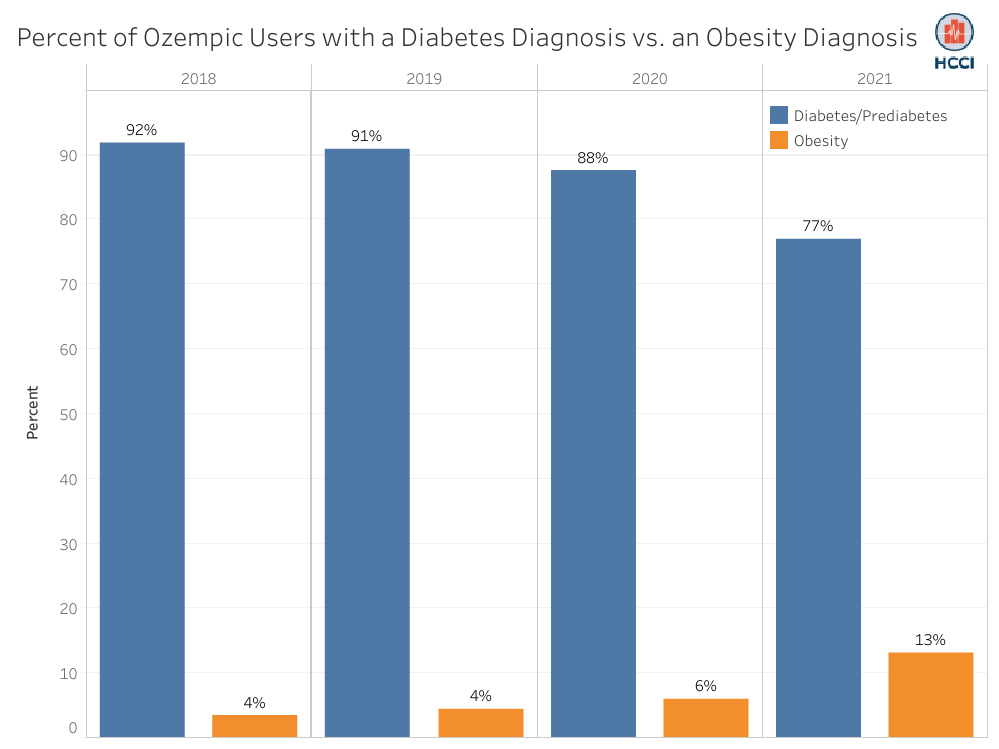 Read more: The Share of Ozempic Users with Diabetes has Decreased Over Time, Indicating Increased Off-label Use
Read more: The Share of Ozempic Users with Diabetes has Decreased Over Time, Indicating Increased Off-label UseOzempic, a relatively new anti-diabetes drug, has been in the headlines because of widespread shortages that are making it difficult for patients who use the drug to manage diabetes to access it. Some news articles suggest that off-label use for weight loss has been a factor associated with increased demand. The active ingredient in Ozempic is…
-
Insulin Prices in ESI Nearly Doubled from 2012-2021, with Effects of Emerging Biosimilars Evident in Recent Years
 Read more: Insulin Prices in ESI Nearly Doubled from 2012-2021, with Effects of Emerging Biosimilars Evident in Recent Years
Read more: Insulin Prices in ESI Nearly Doubled from 2012-2021, with Effects of Emerging Biosimilars Evident in Recent YearsInsulin is a life-saving medication for millions of Americans who live with diabetes. As the price of insulin has risen, people who depend on insulin have had to make difficult decisions about whether to pay for their medication or other necessities. Some have been forced to ration their supply, with devastating results. Recent legislation has limited insulin out-of-pocket costs at…
-
HCCI Spotlights National Diabetes Month: ESI Enrollees with Diabetes Face High Out-of-Pocket Costs. A Cap on Insulin Costs Would Help Many.
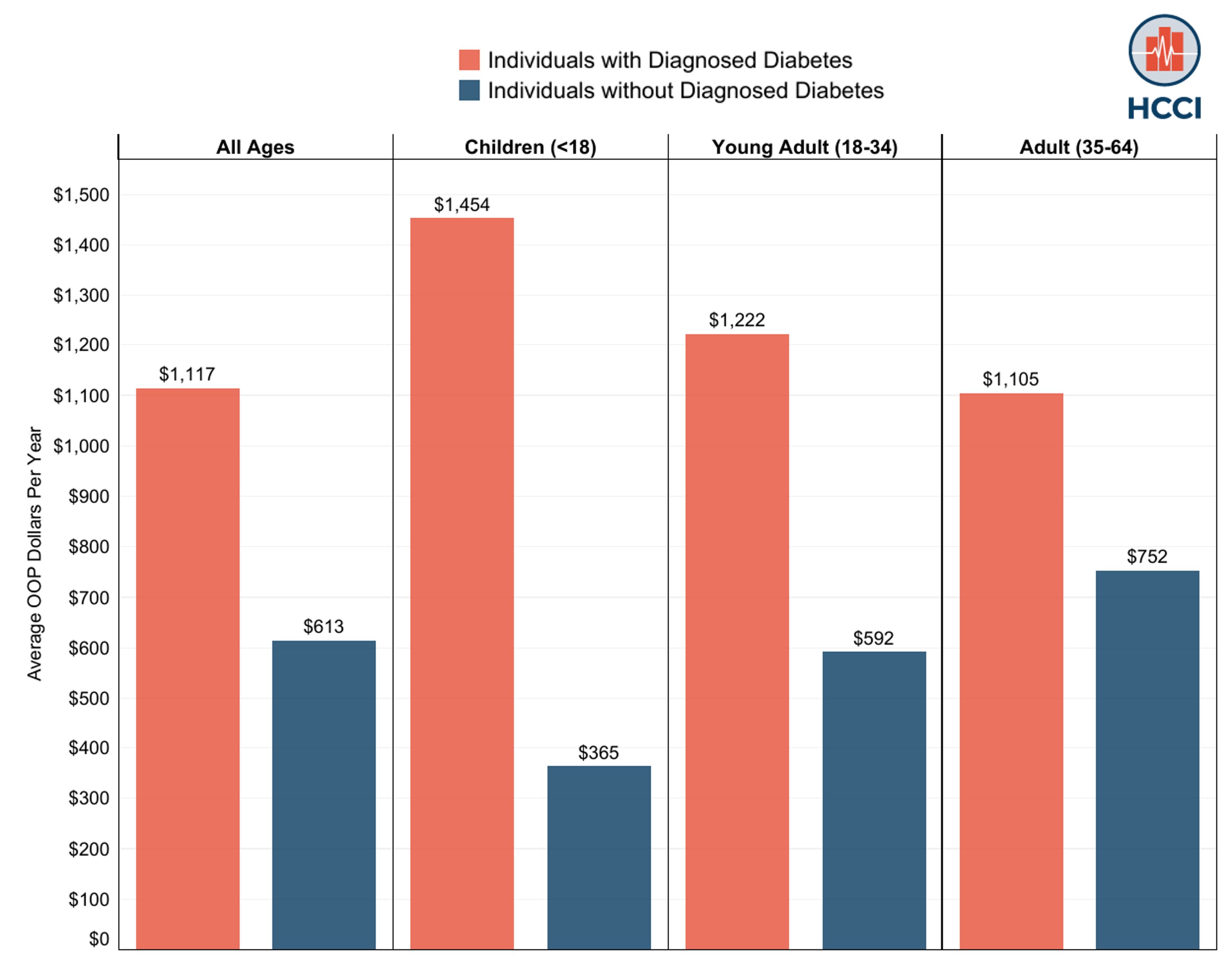 Read more: HCCI Spotlights National Diabetes Month: ESI Enrollees with Diabetes Face High Out-of-Pocket Costs. A Cap on Insulin Costs Would Help Many.
Read more: HCCI Spotlights National Diabetes Month: ESI Enrollees with Diabetes Face High Out-of-Pocket Costs. A Cap on Insulin Costs Would Help Many.Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects over 10% of the U.S. population. It is possible for people who are diagnosed with diabetes to live a healthy, long life if the condition is managed properly. However, management often involves significant health care use, which can be costly for patients. Over the past few months, we used HCCI’s…
-
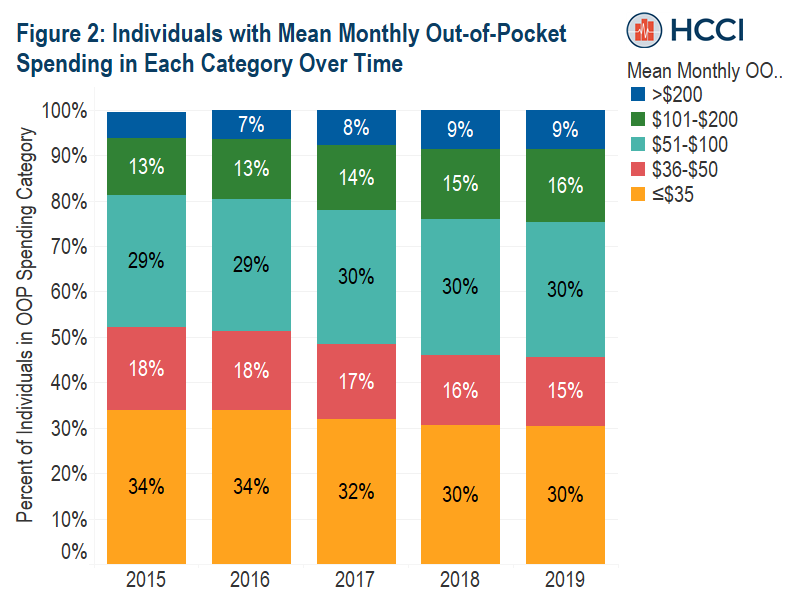
Over 50% of Insulin Users with ESI Spend over $35 Out-of-pocket on 30-day Supply of Insulin
 Read more: Over 50% of Insulin Users with ESI Spend over $35 Out-of-pocket on 30-day Supply of Insulin
Read more: Over 50% of Insulin Users with ESI Spend over $35 Out-of-pocket on 30-day Supply of InsulinPreviously, HCCI analyzed prescription drug spending to understand how many insulin users with employer sponsored insurance (ESI) would be affected by a $35 monthly cap on patient out-of-pocket spending on insulin. Our estimates were based on average monthly out-of-pocket spending on insulin across all insulin products. The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) recently passed by Congress…
-
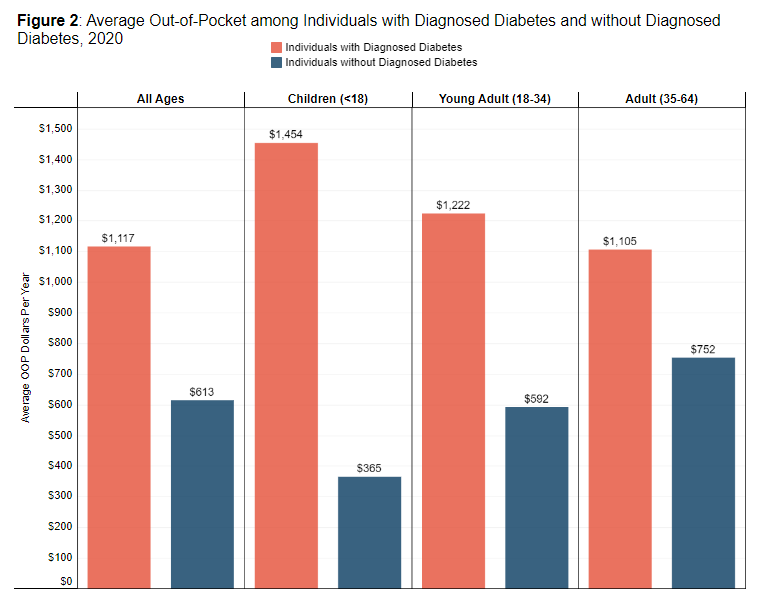
Privately Insured Individuals with Diabetes Spend Twice as Much Out-of-Pocket on Health Care as those without Diabetes
Read more: Privately Insured Individuals with Diabetes Spend Twice as Much Out-of-Pocket on Health Care as those without DiabetesOver 10% of the U.S. population— more than 34 million individuals— lives with diabetes, with 1.5 million new cases diagnosed each year. As people with diabetes manage this chronic condition, they often pay substantial amounts out of their own pockets on medical care and prescription medications. Using HCCI’s unique health care claims dataset, this brief…
-
Capping Out-of-Pocket Spending on Insulin would Lower Costs for a Substantial Proportion of Commercially Insured Individuals
 Read more: Capping Out-of-Pocket Spending on Insulin would Lower Costs for a Substantial Proportion of Commercially Insured Individuals
Read more: Capping Out-of-Pocket Spending on Insulin would Lower Costs for a Substantial Proportion of Commercially Insured IndividualsPrevious HCCI analysis documented rapid growth in insulin spending over the 2012-17 period. High out-of-pocket spending may deter adherence to insulin among individuals with diabetes, with potentially fatal effects. In this blog, we update our analysis of out-of-pocket insulin spending to 2019 using HCCI’s unique commercial claims dataset, which includes prescription drug claims for 29 million…
-
Insulin Use Explains Variation in Level, but not Growth, of Out-of-Pocket Spending on Insulin Products
 Read more: Insulin Use Explains Variation in Level, but not Growth, of Out-of-Pocket Spending on Insulin Products
Read more: Insulin Use Explains Variation in Level, but not Growth, of Out-of-Pocket Spending on Insulin ProductsWe previously published two blogs discussing trends in out-of-pocket spending on insulin products. First, we presented data illustrating how average monthly out-of-pocket spending in 2017 varied considerably by month, particularly for individuals enrolled in consumer-directed health plans (CDHPs) that carry higher deductibles. Second, we examined the relationship between increasing point-of-sale prices between 2012 and 2017…
-
Rising Point-of-Sale Prices for Insulin Correspond with Higher Out-of-Pocket Spending on Insulin in January
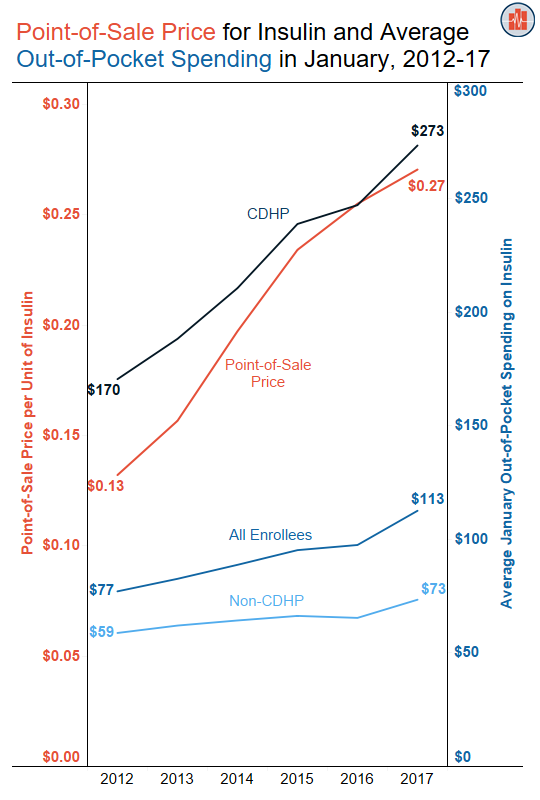 Read more: Rising Point-of-Sale Prices for Insulin Correspond with Higher Out-of-Pocket Spending on Insulin in January
Read more: Rising Point-of-Sale Prices for Insulin Correspond with Higher Out-of-Pocket Spending on Insulin in JanuaryEarlier this week we presented data on out-of-pocket spending on insulin during each month in 2017. In that blog, we showed that enrollees in employer-sponsored health insurance paid more out-of-pocket for insulin products at the beginning of the calendar year. We examined the relationship between increasing point-of-sale prices for insulin and higher out-of-pocket spending in…
-
Out-of-Pocket Spending on Insulin is Highest at the Beginning of the Year
Tags: Commercially Insured, Consumer-Directed Health Plans, Diabetes, Drug Spending, Geographic Variation, Insulin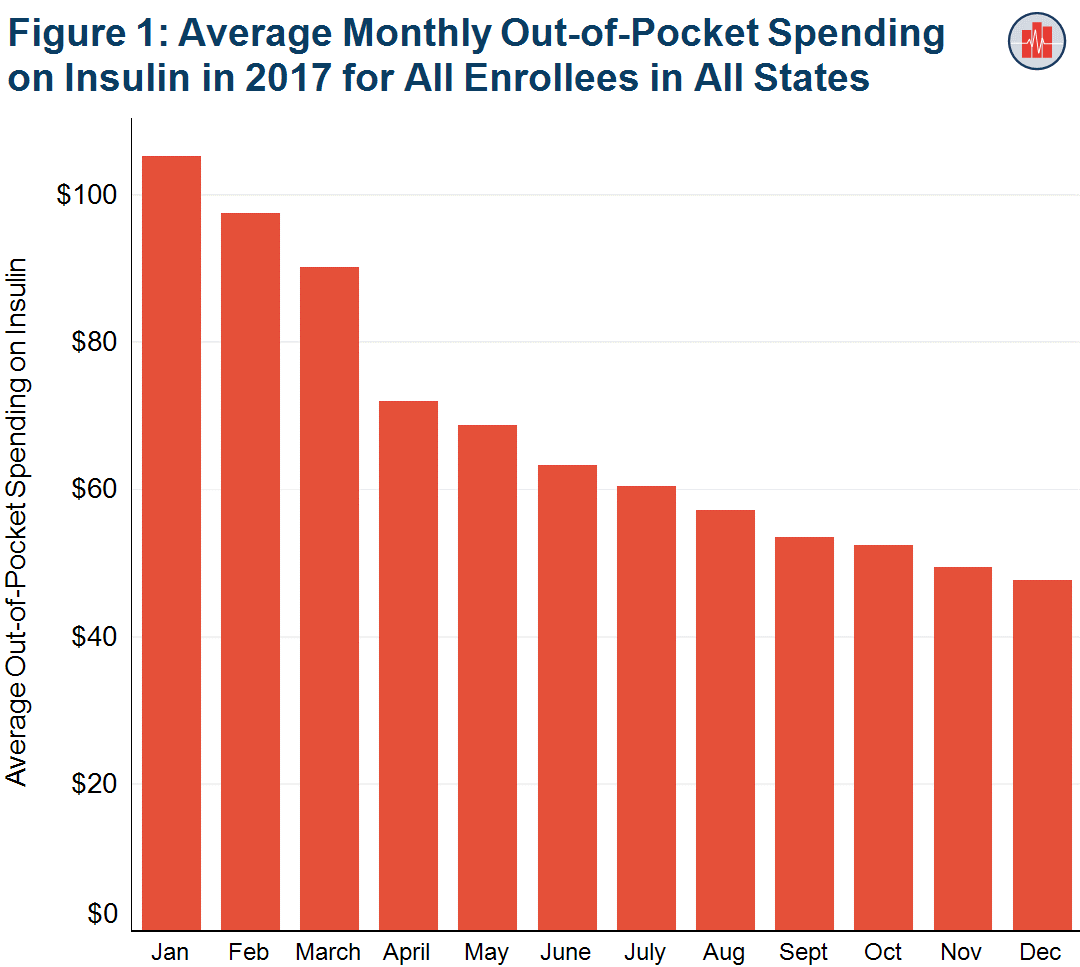 Read more: Out-of-Pocket Spending on Insulin is Highest at the Beginning of the Year
Read more: Out-of-Pocket Spending on Insulin is Highest at the Beginning of the YearPeople who get health insurance through their jobs pay more than twice as much for insulin at the beginning of the year than they do at the end of the year, on average. New analysis of HCCI data shows that, nationally, in January 2017, average out-of-pocket spending on insulin was $105. This spending declined every…
-
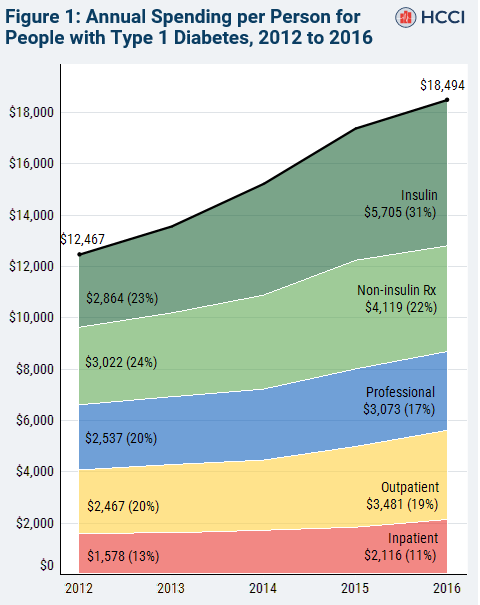
Spending on Individuals with Type 1 Diabetes and the Role of Rapidly Increasing Insulin Prices
Read more: Spending on Individuals with Type 1 Diabetes and the Role of Rapidly Increasing Insulin PricesWe used health care claims data to investigate trends in total health care spending on individuals with type 1 diabetes between 2012 and 2016. We found a rapid increase in total health care spending, driven primarily by gross spending on insulin that doubled over the period. During that time insulin use rose only modestly. While…