Drug Spending
-
International Comparisons of Health Care Prices from the 2024 iFHP Study
Tags: Drug Spending, HCCUR, Inpatient Spending, Out-of-Pocket, Outpatient Spending, Physician Spending, Prices, Utilization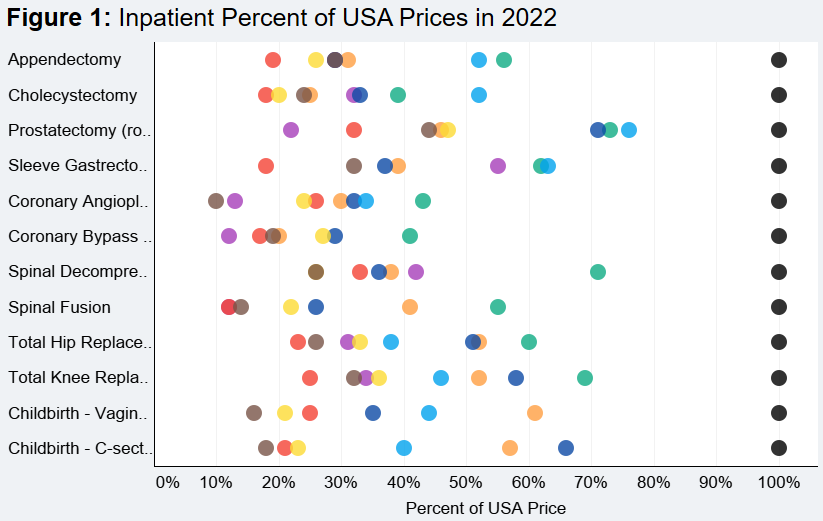 Read more: International Comparisons of Health Care Prices from the 2024 iFHP Study
Read more: International Comparisons of Health Care Prices from the 2024 iFHP StudyThe International Federation of Health Plans (iFHP) has published its 2024 International Healthcare Cost Comparison Report, marking its latest biennial analysis of global healthcare costs. Compiled in collaboration with the Health Care Cost Institute (HCCI), the report compares costs for inpatient and outpatient treatments, as well as prescription drugs, across nine countries using data from…
-
The Share of Ozempic Users with Diabetes has Decreased Over Time, Indicating Increased Off-label Use
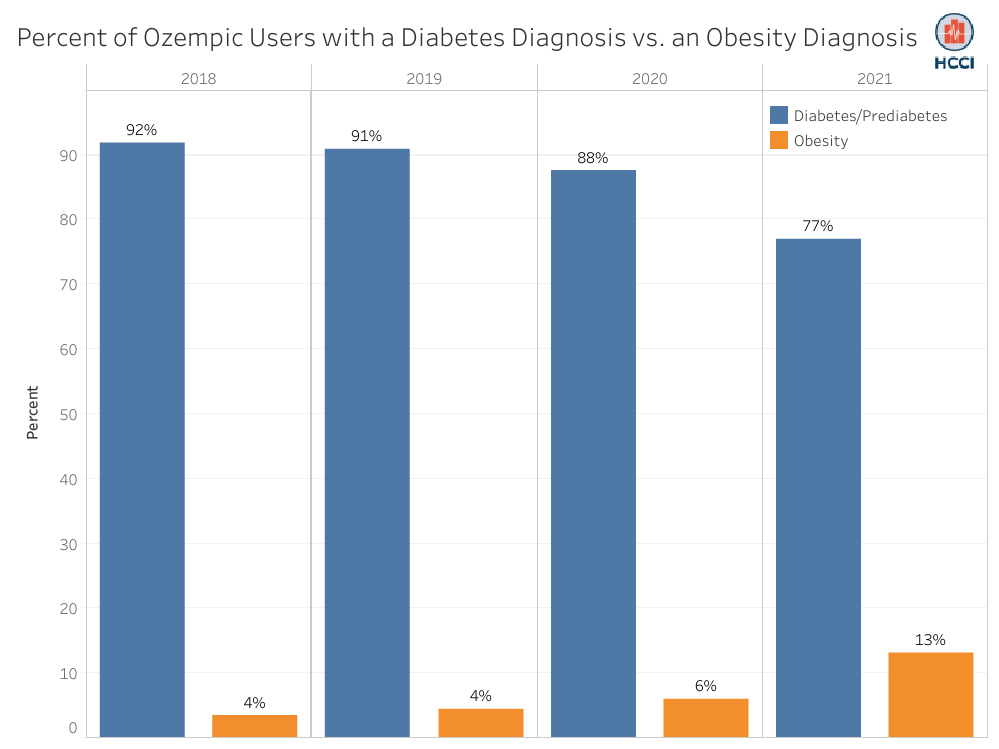 Read more: The Share of Ozempic Users with Diabetes has Decreased Over Time, Indicating Increased Off-label Use
Read more: The Share of Ozempic Users with Diabetes has Decreased Over Time, Indicating Increased Off-label UseOzempic, a relatively new anti-diabetes drug, has been in the headlines because of widespread shortages that are making it difficult for patients who use the drug to manage diabetes to access it. Some news articles suggest that off-label use for weight loss has been a factor associated with increased demand. The active ingredient in Ozempic is…
-
Use of and Spending on Top Prescription Drugs in Employer Sponsored Insurance, 2021
 Read more: Use of and Spending on Top Prescription Drugs in Employer Sponsored Insurance, 2021
Read more: Use of and Spending on Top Prescription Drugs in Employer Sponsored Insurance, 2021Recent policy and other initiatives aim to reduce spending on prescription drugs. At the federal level, the Inflation Reduction Act targets reductions in drug spending in Medicare through price negotiation, capping out-of-pocket spending by patients, and requiring drug manufacturers to pay rebates when prices rise faster than inflation. At the state level, there are initiatives…
-
Uptake of Biosimilars Remains Low Among People with Employer-Sponsored Insurance
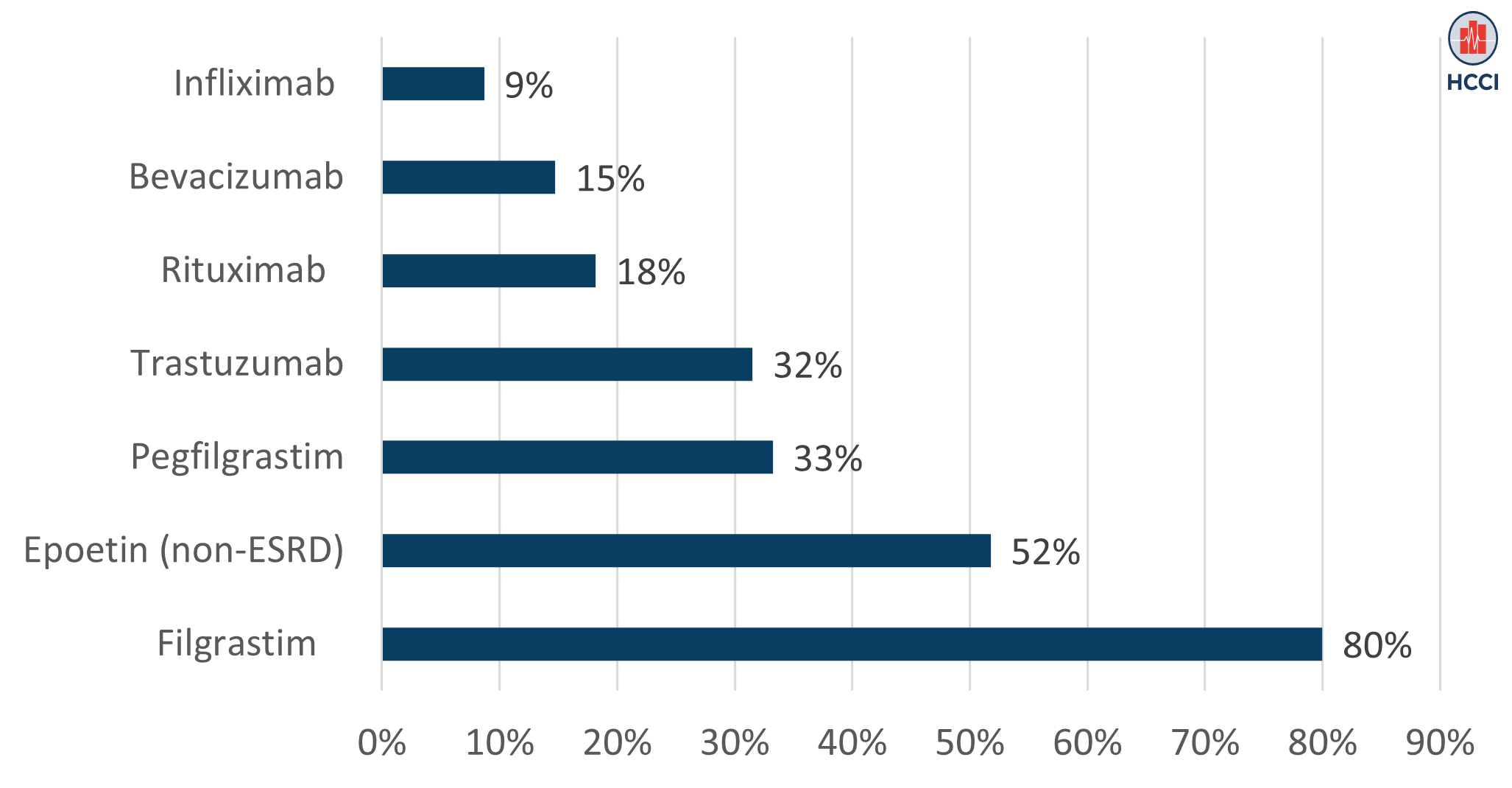 Read more: Uptake of Biosimilars Remains Low Among People with Employer-Sponsored Insurance
Read more: Uptake of Biosimilars Remains Low Among People with Employer-Sponsored InsuranceBiologic drugs represent advances in medical research and treatment but are a major driver of drug spending in the United States. Spending on biologics increased by 50% between 2014 and 2018 in the U.S. even though just 2% of Americans used them. Biosimilars, clinically equivalent, lower-cost versions of original biologic drugs, analogous to generic versions…
-
Trends in HIV PrEP utilization, spending, and price
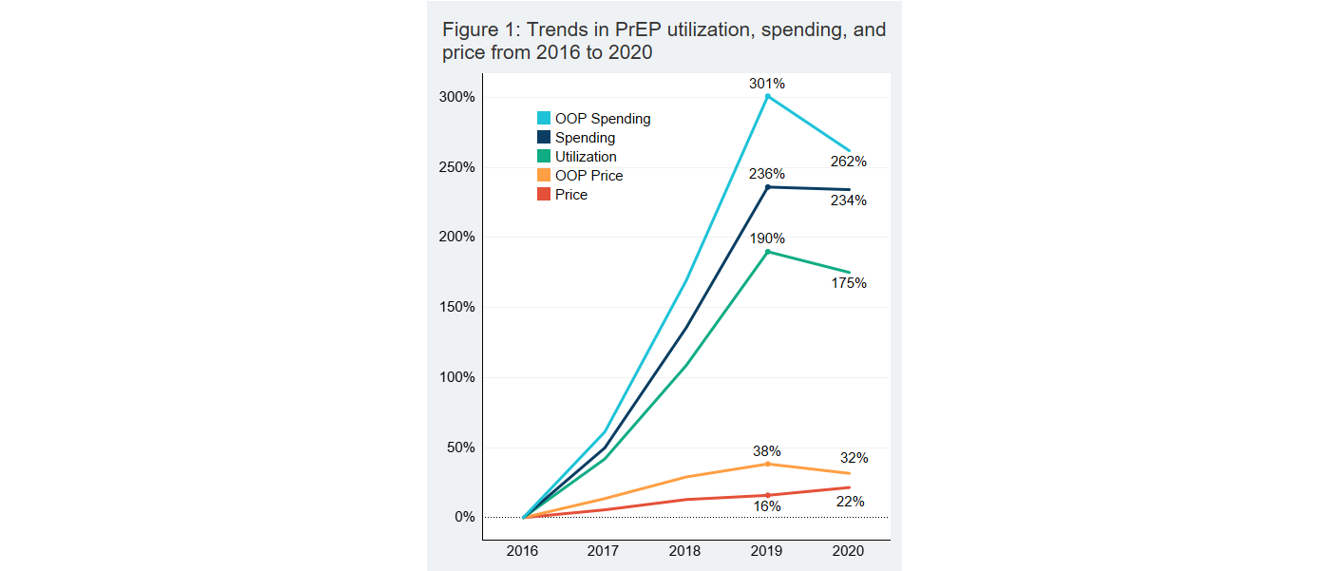 Read more: Trends in HIV PrEP utilization, spending, and price
Read more: Trends in HIV PrEP utilization, spending, and pricePre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) for HIV are medications that reduce an individual’s chances of contracting HIV. The CDC estimates that 1.2 million people are at risk of HIV infection and may benefit from a PrEP prescription. We analyzed health insurance claims for 55 million Americans with employer-sponsored insurance in order to examine utilization and spending on…
-
HCCUR Data Point: Trends in Total (Administered and Prescription) Drug Spending in ESI
 Read more: HCCUR Data Point: Trends in Total (Administered and Prescription) Drug Spending in ESI
Read more: HCCUR Data Point: Trends in Total (Administered and Prescription) Drug Spending in ESITotal spending on drugs includes spending on prescription drugs (typically oral medications prescribed by a physician, picked up by a patient at a local pharmacy, and taken at home) and administered drugs (typically injected or infused under the supervision of a health care professional either in an outpatient facility or physician office). In HCCI’s Health Care Cost…
-
International comparisons of health care prices from the 2017 iFHP survey
Tags: Administered Drugs, Commercially Insured, Drug Spending, Inpatient Spending, Outpatient Spending, Prices Read more: International comparisons of health care prices from the 2017 iFHP survey
Read more: International comparisons of health care prices from the 2017 iFHP surveyThe International Federation of Health Plans (iFHP), a CEO network of the global health insurance industry based in London, in partnership with the Health Care Cost Institute (HCCI) in the United States, and iFHP member companies in eight countries, today published the latest International Comparison of Health Prices Report. The report compares the median prices…
-
Insulin Use Explains Variation in Level, but not Growth, of Out-of-Pocket Spending on Insulin Products
 Read more: Insulin Use Explains Variation in Level, but not Growth, of Out-of-Pocket Spending on Insulin Products
Read more: Insulin Use Explains Variation in Level, but not Growth, of Out-of-Pocket Spending on Insulin ProductsWe previously published two blogs discussing trends in out-of-pocket spending on insulin products. First, we presented data illustrating how average monthly out-of-pocket spending in 2017 varied considerably by month, particularly for individuals enrolled in consumer-directed health plans (CDHPs) that carry higher deductibles. Second, we examined the relationship between increasing point-of-sale prices between 2012 and 2017…
-
Rising Point-of-Sale Prices for Insulin Correspond with Higher Out-of-Pocket Spending on Insulin in January
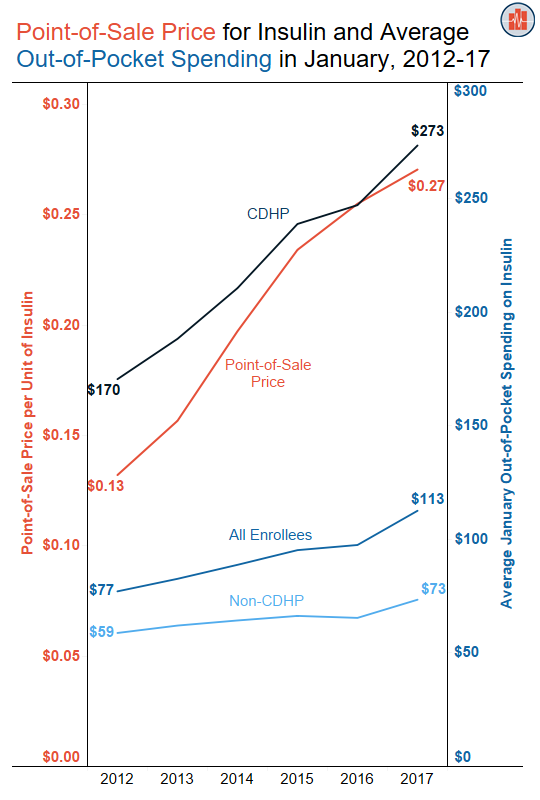 Read more: Rising Point-of-Sale Prices for Insulin Correspond with Higher Out-of-Pocket Spending on Insulin in January
Read more: Rising Point-of-Sale Prices for Insulin Correspond with Higher Out-of-Pocket Spending on Insulin in JanuaryEarlier this week we presented data on out-of-pocket spending on insulin during each month in 2017. In that blog, we showed that enrollees in employer-sponsored health insurance paid more out-of-pocket for insulin products at the beginning of the calendar year. We examined the relationship between increasing point-of-sale prices for insulin and higher out-of-pocket spending in…
-
Out-of-Pocket Spending on Insulin is Highest at the Beginning of the Year
Tags: Commercially Insured, Consumer-Directed Health Plans, Diabetes, Drug Spending, Geographic Variation, Insulin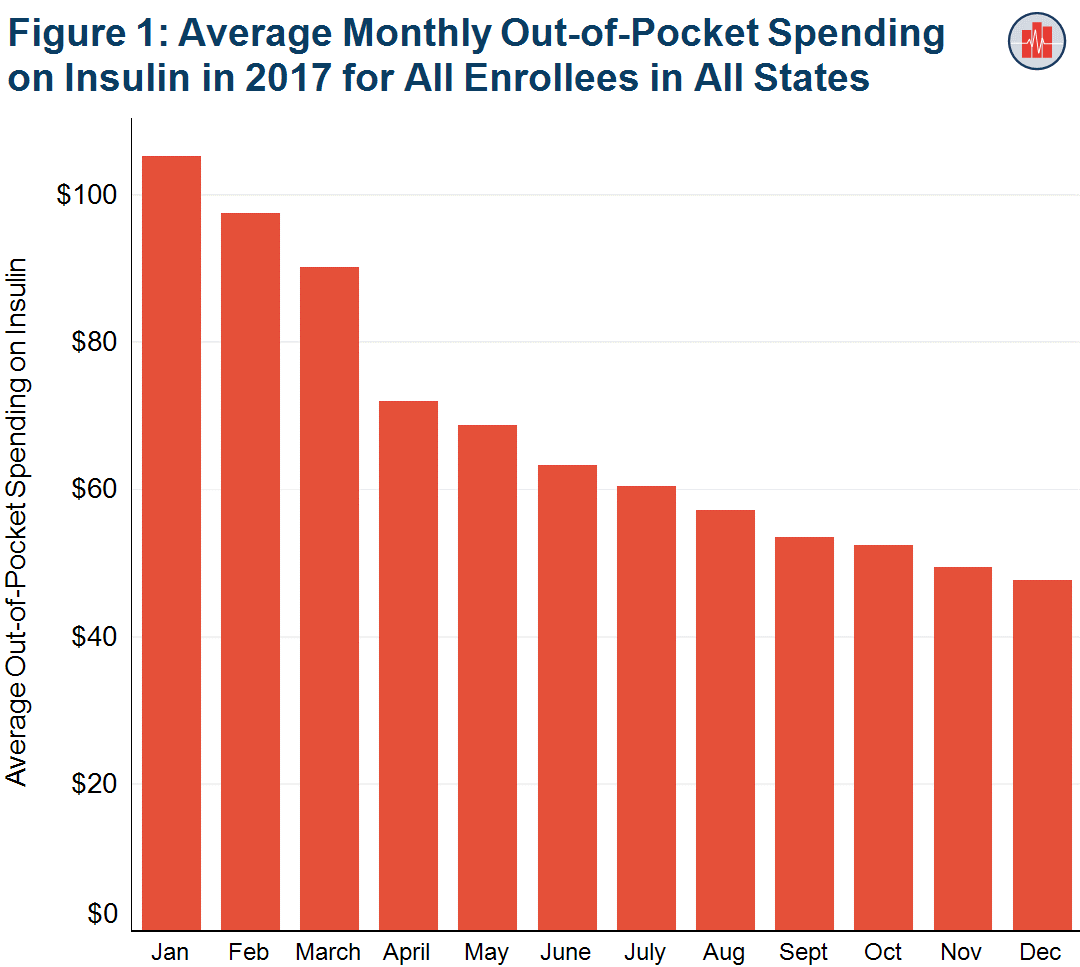 Read more: Out-of-Pocket Spending on Insulin is Highest at the Beginning of the Year
Read more: Out-of-Pocket Spending on Insulin is Highest at the Beginning of the YearPeople who get health insurance through their jobs pay more than twice as much for insulin at the beginning of the year than they do at the end of the year, on average. New analysis of HCCI data shows that, nationally, in January 2017, average out-of-pocket spending on insulin was $105. This spending declined every…
